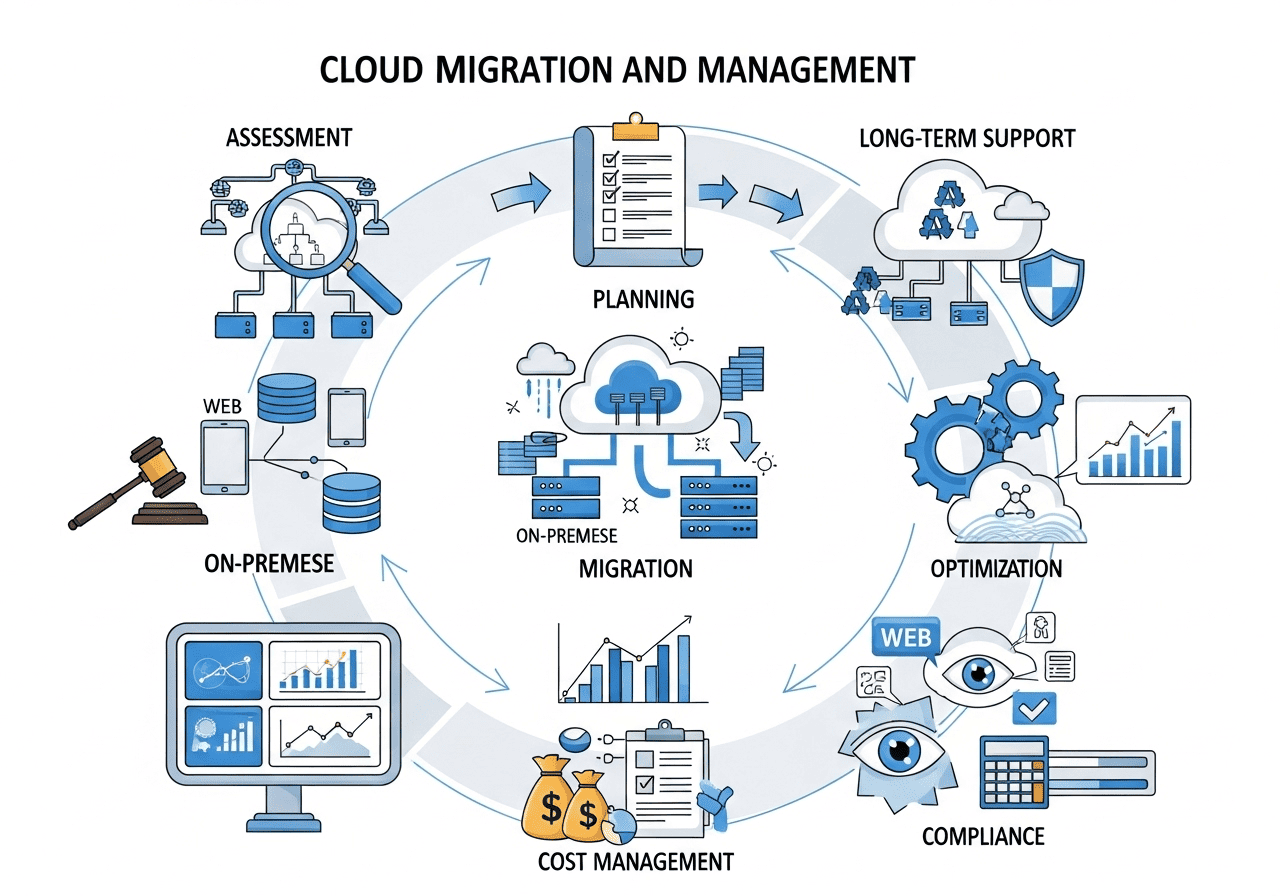
What is a cloud migration roadmap and why is it important?
A cloud migration roadmap is a strategic plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources required to move workloads to the cloud. It provides a structured approach to manage complexity, prioritise critical applications, and ensure security. By following a roadmap, organisations can reduce risks, avoid downtime, and make informed decisions. It also enables teams to coordinate effectively, maintain business continuity, and gain confidence throughout the migration process.
How do you prioritise workloads in a migration roadmap?
Prioritising workloads involves assessing business impact, complexity, and dependencies. Critical systems that affect revenue or operations are usually migrated first using careful planning. Less critical or standalone applications can be moved later to test processes. Evaluating resource requirements, data sensitivity, and integration needs ensures smooth sequencing. This approach reduces risk, allows incremental validation, and ensures that essential workloads continue functioning without disruption during the migration.
What role does risk assessment play in a cloud migration roadmap?
Risk assessment identifies potential challenges such as data loss, downtime, compatibility issues, and security vulnerabilities. Including it in the roadmap allows teams to implement mitigation strategies like backups, phased transfers, and monitoring. By anticipating obstacles, organisations can plan contingencies, reduce operational disruptions, and ensure workloads are migrated safely. A thorough risk assessment increases confidence, strengthens planning, and safeguards both systems and data throughout the migration.
How does a roadmap help manage complex workloads?
Complex workloads often involve multiple interdependent applications and large datasets. A roadmap breaks down the migration into manageable stages, defining dependencies and sequencing steps. This structured approach allows teams to test each component, validate integrations, and prevent errors. By planning resource allocation and monitoring progress, organisations can migrate even highly complex workloads with confidence, ensuring minimal operational impact and maintaining system performance throughout the transition.
Why is backup and recovery planning included in a roadmap?
Backup and recovery planning ensures that critical data can be restored if issues arise during migration. A roadmap defines backup frequency, storage locations, and validation procedures. Having recovery steps in place protects against accidental data loss, corruption, or system failure. This proactive approach safeguards operations, provides peace of mind, and allows teams to proceed confidently, knowing that workloads can be recovered without affecting business continuity.
How can phased migration reduce risk in the roadmap?
Phased migration moves workloads incrementally rather than all at once, allowing teams to validate each stage before proceeding. This approach mitigates risk by isolating potential issues to a small set of applications. It also provides time for troubleshooting and optimisation, reducing the chance of downtime. Including phased migration in the roadmap ensures controlled execution, maintains operational continuity, and builds confidence in the migration of complex systems.
How does monitoring enhance a cloud migration roadmap?
Monitoring tracks data transfers, application performance, and system health during migration. Real-time alerts allow teams to respond quickly to anomalies, preventing disruption. Monitoring ensures that workloads are correctly transferred, performance meets requirements, and security is maintained. Including monitoring in the roadmap improves visibility, accountability, and proactive management, enabling safe and confident migration of critical and complex workloads without impacting daily operations.
Why is stakeholder communication important in a migration roadmap?
Effective stakeholder communication keeps teams, management, and end-users informed about migration timelines, progress, and potential impacts. A roadmap outlines communication responsibilities and frequency, ensuring expectations are managed. Clear communication helps coordinate cross-functional teams, prevent misunderstandings, and quickly address concerns. It also builds trust, supports smooth adoption, and ensures that everyone is prepared for the transition, reducing the risk of operational disruptions.
How does testing fit into a cloud migration roadmap?
Testing validates that applications, systems, and data function correctly before and after migration. The roadmap includes pre-migration tests to identify potential issues and post-migration validation to confirm successful implementation. Testing ensures data integrity, system performance, and user accessibility, preventing unexpected disruptions. Including testing in the roadmap provides a structured approach to identify and fix issues early, ensuring workloads are migrated safely and with minimal risk.
What is the role of security planning in the roadmap?
Security planning protects sensitive data and critical applications during migration. The roadmap should define encryption methods, access controls, secure transfer protocols, and compliance checks. By integrating security measures at every stage, organisations prevent breaches and maintain regulatory compliance. Security planning ensures workloads are safely transferred, reduces operational risks, and gives stakeholders confidence that systems and data remain protected throughout the migration.
How can resource allocation be optimised in the roadmap?
Resource allocation ensures sufficient computing power, storage, and network bandwidth are available for workloads during migration. The roadmap outlines requirements for each stage, preventing performance bottlenecks or failures. Proper allocation allows IT teams to balance workloads, monitor usage, and scale resources as needed. Optimising resource allocation ensures smooth migration, maintains system performance, and supports operational continuity while moving complex workloads to the cloud.
Why are rollback procedures included in the roadmap?
Rollback procedures provide a safety mechanism to revert workloads to their previous state if migration issues occur. The roadmap defines conditions for rollback, steps to execute it, and validation checks. This ensures that critical systems remain operational and prevents prolonged downtime or data loss. Including rollback strategies enhances confidence in executing complex migrations and allows organisations to manage unforeseen challenges safely and effectively.
How can roadmap timelines improve migration efficiency?
Timeline planning sets clear deadlines for each migration stage, helping teams prioritise tasks and coordinate efforts. By allocating realistic time for data transfer, testing, and validation, organisations reduce the risk of rushed decisions and errors. Timelines also help manage dependencies between applications, ensuring smooth progression. A well-defined roadmap timeline increases efficiency, maintains operational continuity, and ensures complex workloads are migrated safely and systematically.
How does post-migration optimisation fit into the roadmap?
Post-migration optimisation involves monitoring performance, tuning systems, and adjusting workflows for efficiency in the cloud environment. The roadmap includes these steps to ensure workloads operate optimally and resources are used effectively. This stage identifies potential improvements, resolves residual issues, and ensures end-users experience seamless functionality. Including optimisation in the roadmap guarantees long-term performance, scalability, and stability after complex workloads have been migrated.
Why should enterprises review and update the roadmap regularly?
Regular review and updates ensure the roadmap reflects current business priorities, infrastructure changes, and lessons learned from ongoing migration activities. Continuous evaluation helps identify risks, adjust timelines, and incorporate feedback from teams. By keeping the roadmap current, organisations maintain alignment with strategic objectives, ensure smooth execution, and build confidence in managing complex workloads, ultimately supporting a safe and successful cloud migration process.